- Industries & Machines Industries & Machines
- IIoT IIoT
- Service-Toll Processing Service-Toll Processing
- Material Material
- News News
- IR Information IR Information
-
Sustainability
Sustainability
Sustainability
- Introduction
- Sustaibality Policy - Mission Statement
- Editorial Policy
- Materiality & Strategy
- Technological contribution to a sustainable global environment
- Contributions towards a safer, more secure and prosperous society
- Sophistication of governance that supports business
- ESG Data Collection
- Sustainable Business Management ~ Finance
- Infromation Disclosure Based on TCFD Recommendations
- Jobs and Careers Jobs and Careers
-
About Us
About Us
About Us
- Corporate Vision
- Greetings (Company Introduction)
- Corporate Overview
- Corporate Profile
- Business Areas and Strengths
- Corporate History
- Hosokawa Micron Group
- Domestic Facilities
- Overseas Subsidiaries (Asia)
- Overseas Subsidiaries (Europe)
- Overseas Subsidiaries (America)
- Asian Agents
- Powder Technology Research Institute
- Industrial Property Rights
- Journals and Books
- Technical Information
- Annual Publication "Micromeritics"
- Compliance Charter
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Quality Principle

Industries & Machines
- TOP
- Industries & Machines
- Machines Search
- Fluidized Bed Opposed Jet Mills AFG, AFG-CRS[NEW!]
Fluidized Bed Opposed Jet Mills AFG, AFG-CRS[NEW!]

Summary
Hosokawa introduced the fluidized bed opposed jet mill onto the market in 1981, revolutionizing the sector of jet milling. Since then, almost 1000 systems with fluidized bed opposed jet mills have been delivered for an enormous variety of different applications, and Hosokawa's fund of know-how in this field is correspondingly immense.
Principle
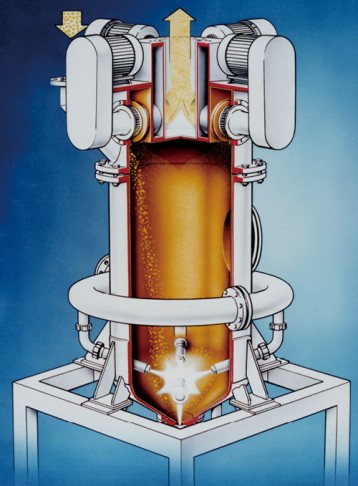
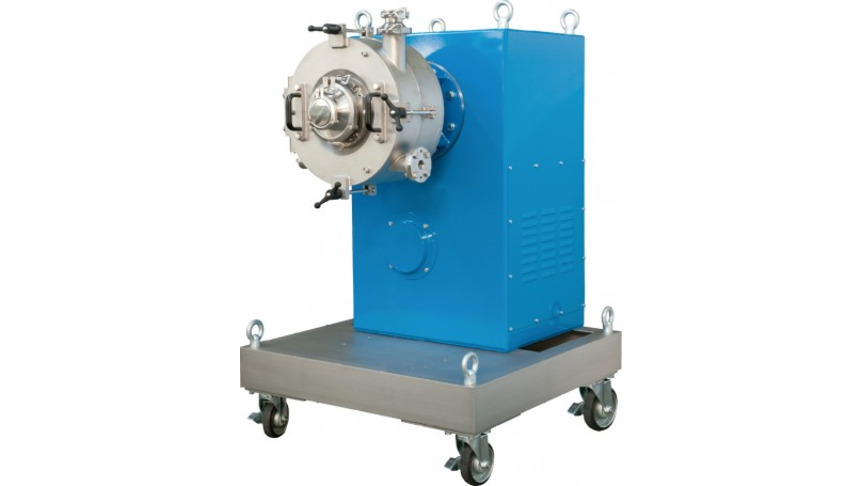
Fig.1 Fluidized bed opposed jet mill AFG-R

Fig.2 Grinding chamber with Megajet nozzles

Fig.3 400/1 AFG on load cell
In the case of jet milling, one takes advantage of the fact that as compressed gas exits a nozzle, it is accelerated to extremely high speeds. In expanding, the energy contained in the compressed gas in the form of heat is converted to kinetic energy. The speed of sound is initially a natural limit for the exit velocity. But by using Laval nozzles, the exit velocity can be increased to above the speed of sound. Laval nozzles are characterized by their hourglass shape, which widens downstream of the narrowest cross-sectional point, the nozzle throat. The length of the divergent part of the nozzle is adapted to suit the operating pressure. Compressed air of 20°C at 0.6MPa overpressure is frequently used as the grinding gas, and delivers nozzle exit speeds of around 500 m/s. As a result of drawing in gas and product from the fluidized bed, the speed of the gas jets blasts extremely rapidly after exiting the nozzles. Comminution is a result of interparticle collision in the jets of air and also in the core area, i.e. the point where the opposing jets intersect.
Jet mills are impact mills which are used to achieve maximum fineness values. Such particle sizes can only be obtained in connection with an air classifying step. Spiral jet mills have a static air classifier integrated into the mill housing, whereas fluidized bed opposed jet mills are equipped with a dynamic deflector-wheel classifier. The fineness is set as a function of the classifying wheel speed.
The most important is a high product loading at the nozzle jets in order to achieve a high concentration of particles and thus high impact probabilities. The patented Megajet nozzles were developed with this in mind. They consist of four small nozzles which as a result of their close proximity generate an under pressure at their common centre, and thus draw particles from the fluidized bed direct into the centre of the nozzle jet. The product level in the machine is controlled by means of load cells or by monitoring the current loading of the classifier drive.
Parameter
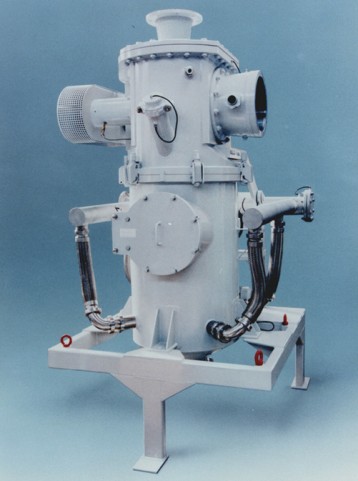
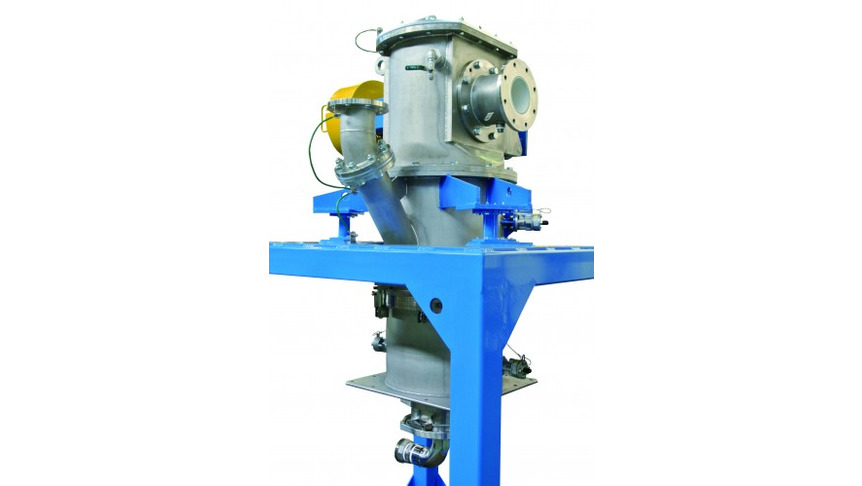
Fig.4 710/1 AFG for products that tend to deposit
The mechanical jet power not only increases as a function of the gas flow rate but also as a function of the grinding gas pressure and temperature. Different conditions of the grinding gas, e.g. pressures, temperatures, have to be compared on the basis of the mechanical jet power. During compression, the grinding gas heats up. However, the less it is cooled, the more energy is transported to the nozzles and is then available for the size reduction. If the product permits, running the mill in hot-gas mode will increase the efficiency of the grinding system. The efficiency of compressed air generation is at its best if it is possible to work with low pressures, i.e. with a one-stage compressor.
Specifications(AFG Model)
- Single-/multi-wheel classifier head
- Monobloc ceramic classifying wheels
- Stainless steel or mild steel
- Horizontal or 3D nozzle arrangement
- Lining: PU, ceramic, special-grade steel
- Hot-gas mode for mineral products
- Load cells for product level control
- Megajet nozzles
- Explosion-pressure-shock-proof to 1.1MPa with type test certificate as defined in 94/9/EC
- Pharma design up to machine size 630 AFG
- Closed-circuit gas systems for pyrophoric products.
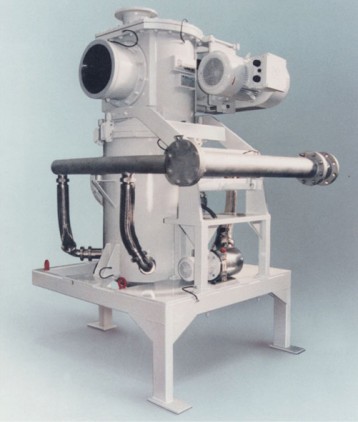
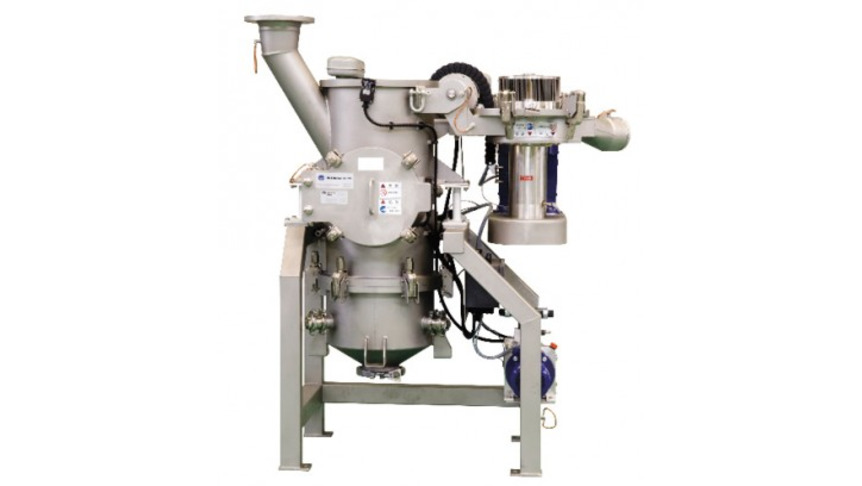
Fig.5 800/1 AFG pressure shock proof to 1.1MPa with hydraulic mechanism to open and close the classifier head

Fig.6 400/1 AFG in production plant

Fig.7 710/4 AFG for special ceramics, wear protected design with monobloc ceramic classifying wheels
Applications:
Even difficult products can be processed efficiently with AFG jet mills.
- Ceramic materials such as oxides, carbides, nitrides, silicates
- Abrasives, polishing and lapping compounds
- High-performance magnetic materials based on rare earth metals such as neodymium iron boron and samarium cobalt.
- Highly pure materials, e.g. fluorescent powders, silica gels.
- Plant protectors
- Pharmaceutical products
- Resins, wax
- Pigments and dyestuffs
- Mineral powders
- Selectively ground composite materials such as metal alloys.
AFG-CRS Model
General information
A jet mill suitable for ultra fine millng of various products due to integrated ultra fine classifier with easy disassembly for maintenance.
Principle

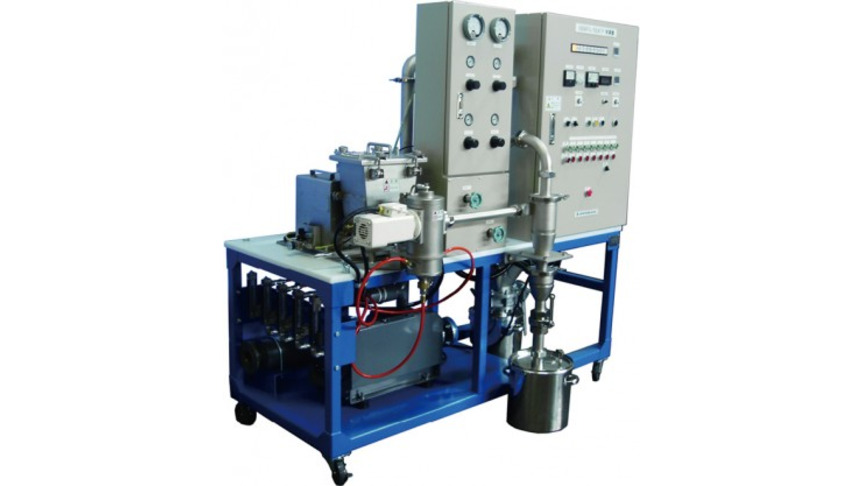
Fig.8 Disassembly of 200AFG-CRS
The classifying wheel is designed on basis of the forced and semifree vortex theory, resulting in sub-micron classification. Combined with opposed jet mill technology, sub-micron grinding is achieved. CRS wheels are made in ceramics for metal contamination free application.
Features
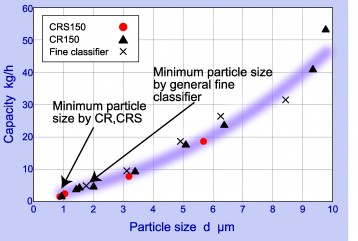
Fig.9 Comparison to general jet mill and CR model (Talc grinding)
- Ultra fine grinding with integrated ultra fine classifier
- Easy disassembly for maintenance compared to conventional CR model
- The minimum partiicle size and grinding efficiency are equal to conventional CR model
- No metal contamination in ceramics model
- Scale up with same product size with multi-wheel classifiers
Applications
- Electric material (Glass, Sealing agent, etc.)
- Graphite, Coke (for anode, capacitor material)
- Activated carbon
- MInerals (Calcium carbonate, Talc, etc.)
etc.
Related equipments

Feel free to contact us. if you have any questions or concerns.