- Industries & Machines Industries & Machines
- IIoT IIoT
- Service-Toll Processing Service-Toll Processing
- Material Material
- News News
- IR Information IR Information
-
Sustainability
Sustainability
Sustainability
- Introduction
- Sustaibality Policy - Mission Statement
- Editorial Policy
- Materiality & Strategy
- Technological contribution to a sustainable global environment
- Contributions towards a safer, more secure and prosperous society
- Sophistication of governance that supports business
- ESG Data Collection
- Sustainable Business Management ~ Finance
- Infromation Disclosure Based on TCFD Recommendations
- Jobs and Careers Jobs and Careers
-
About Us
About Us
About Us
- Corporate Vision
- Greetings (Company Introduction)
- Corporate Overview
- Corporate Profile
- Business Areas and Strengths
- Corporate History
- Hosokawa Micron Group
- Domestic Facilities
- Overseas Subsidiaries (Asia)
- Overseas Subsidiaries (Europe)
- Overseas Subsidiaries (America)
- Asian Agents
- Powder Technology Research Institute
- Industrial Property Rights
- Journals and Books
- Technical Information
- Annual Publication "Micromeritics"
- Compliance Charter
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Quality Principle

Industries & Machines
- TOP
- Industries & Machines
- Machines Search
- TorusDisc TD
TorusDisc TD
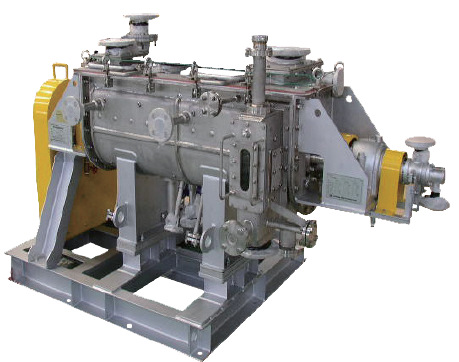
Summary
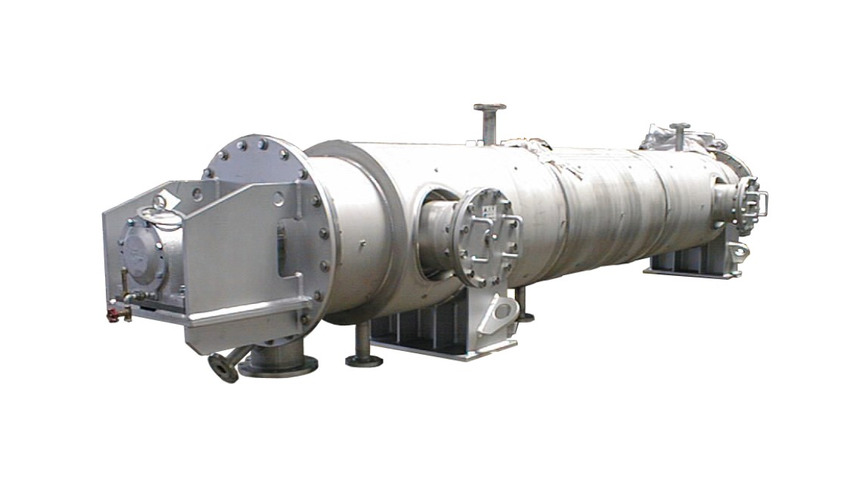
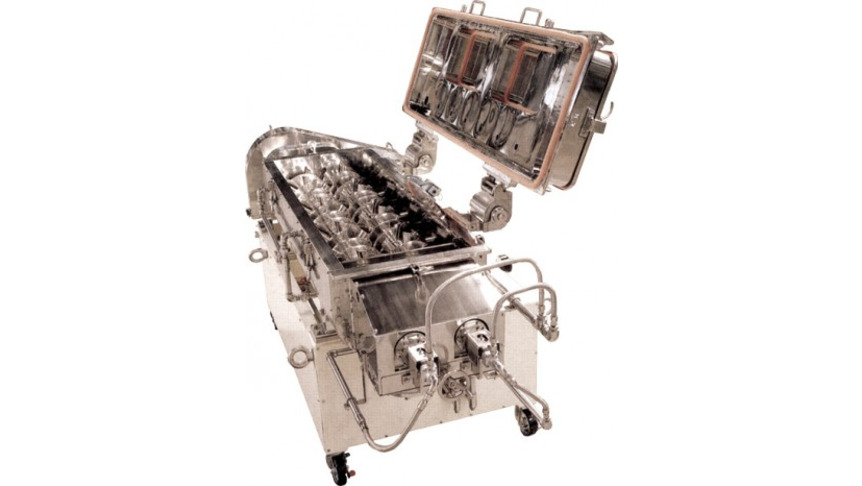
The TorusDisc is the indirect dryer consisting with jacket and torus shaped discs. The material in the dryer receives heat from the outside jacket and the inside discs. The discs cover 80% of the total heating surface. Comparing to the other indirect heating dryer, the TorusDisc has compact design and high thermal efficiency. As the TorusDisc can keep longer residence time, drying at both constant-rate period and decreasing-rate period of drying are possible by one machine. The TorusDisc can cope with drying the material of wide range of moisture contact. The unit can also be used as a cooler by applying water or cooling media.
Comparing to the double shaft dryer, The TorusDisc provides a higher plug flow. Widely applied in the field of resin, food, mineral and chemical.
Principle
The TorusDisc consists of a stationary horizontal vessel, equipped with heating/cooling jacket, providing a tubular rotor with vertically mounted double-walled discs. As heating media (cooling media) hot water, steam, or thermal oil (industrial water, cooling water, or cooling media for cooling) are available to be induced to jacket and rotor. The construction of the disc rotor for steam media is different from that of thermal oil. In case of steam media, the condensation is picked up by dipper pipes along the rotation of discs, and discharged continuously. In case of thermal oil heating, it enters one end of the rotor shaft, passes through each disc and goes out from the other end of shaft. In either construction (steam/oil), the dryer is constructed in the way each disc is evenly heated with uniform temperature distribution.
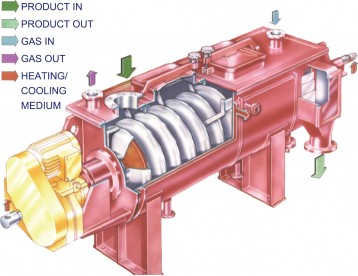
Fig.1 Schematic structure
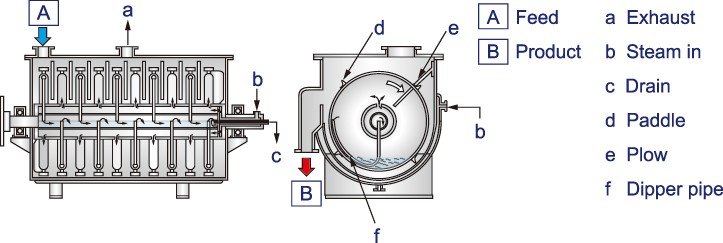
Fig.2 TorusDisc (Heating medium: Steam)

Fig.3 Drying curve
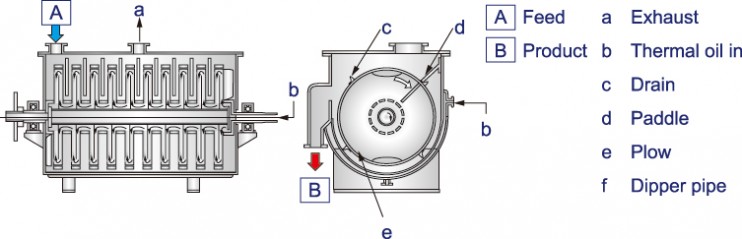
Fig.4 TorusDisc (Heating medium: Liquid)
Feed material is charged at one end of the dryer, and then it is transported through the annular space between the discs and the vessel toward the discharge port. Conveying vanes are fixed to the outer rim of the discs to control conveyance. Stationary agitator plows are located between the discs in order for better mixing of the powder to convey the material to next annular space, and to prevent material build-up on heat transfer surfaces. Thus, the material securely travels between the discs receiving heat transfer, and short passing above the discs are prevented. The functions of the vanes and the plows increase the heat transfer efficiency by agitating/mixing. The dried product is discharged by overflow from the weir placed at the end of the vessel. Adjusting the height of the outlet weir controls residence time. By applying inert gas, such as N2, as a career gas, it is possible to dry volatile solvent, to prevent oxidization of material or moisture absorption by product.
Features
- Compact structure with large heat transfers area. Reduced heat loss to outside, and effective use of heat energy.
- High heat transfer coefficient. For dry powder, heat transfer coefficient is 20-35kJ/m2 h K, wet powder; 30-60kJ/ m2 h K, slurry, 60-230kJ/m2 h K.
- Wide operating application for drying, heating, cooling, vacuum drying and combined operation with hot air.
- Adjustable material hold-up. By adjustment of the conveying vanes and height of overflow weir, material hold-up quantity can be controlled.
- Very limited quantity of carrier gas is required. Ancillary equipment such as gas heater and blower is relatively small. This leads space and energy saving system.
- It is possible to raise the material temperature up to 200°C. Applicable for drying and reaction of heat resistance resin.
Applications
Fig.5 Flow
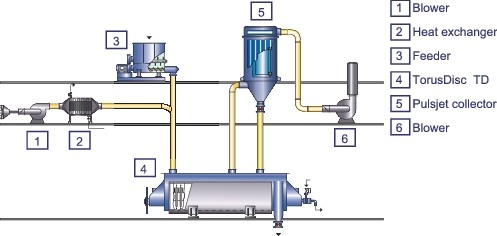
Fig.6 Production plant

Related equipments

Feel free to contact us. if you have any questions or concerns.